SENSE ORGANS
Eye
Transduction--------------------> Conversion of image into signal
Vitreous chamber (VC) --------------------> Vitreous jelly (fixed quantity)
Aqueous chamber(AC) --------------------> Aqueous liquid (daily secreted) --------------------> Drain excess of aqueous liquid through canal of Schlem.
Inter ocular pressure increase because of blockage of canal of Schlem (IOP) -------------------->Glucoma
6 muscles in eye controlled by 3 cranial nerves in human. (Occulomotor-3rd, Trochlear-4th and Abducens-6th )
{SO controlled by 4th and LR by 6th. Other muscles controlled by nerve III} @SO4 LR6
- O---------------->Oblique
- S---------------->Superior
- M---------------->Medial
- I---------------->Inferior
Pupil
Near object--------------------> Less focal length-------------------->Contraction of ciliary muscle-------------------->Thick lens
Retina
Rod cell-------------------->Rhodopsin-------------------->Dimlight vision
Cone cell-------------------->Iodopsin-------------------->Colour detect-------------------->Bright
Glands of eye
Tear/Lacrymal gland
Lysozymes-------------------->Kill infectants
1% solution of NaCl
Meibomian gland
Oily chemical lubricate cornea blinking of eye
Defects of eye
Myopia (Short sightness)
Hypermetropia(Long sightness)
Presbiopia-------------------->Old age (Loss of accommodation of eye) -------------------->Remedy(Bifocal lens)
Astigmatism--------------------> Curvature problem-------------------->Cylindrical lens for remedy
Cataract--------------------> Opaque area in lens
Disease
Xerophthalmia-------------------->dry eye (vit A deficiency)
Night blindness--------------------> vit A deficiency
Trachoma--------------------> Bacterial infection (Chlamydia trachomatic)
EAR
Scala vestibule and tympani connected by helicotrema and contain perilymph. Scala media contain endolymph.
Receptors
- Organ of corti-------------------------------> Sound
- Macula------------------------------->in sacculus and utriculus
- Cristae------------------------------->in ampulla
Macula and cristae hep in balancing movement of head.
Semicircular canals are filled with endolymph and enlargement at one of it’s end is ampulla.
Ear ossicles
Malleus----------------------->Hammer shaped------------------------>Articular bone
Incus------------------------>Anvil shaped------------------------>Hyomandibular bone
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
Mouth
Vibrissae/whiskers------------->upper lip of rabbit
philtrum-------------> upper lip of man
Vestibule-------------> space between lip and teeth/ cheek and gum
Buccal cavity and pharynx separated by isthmus.
Jacobson organ------------->Present on upper jaw of rabbit (take smell)
Palate
- Soft palate------------->Have uvula(Uvula or venum)
- Hard palate------------->Have rugae
Teeth of mammal------------->thecodont, diphyodont, heterodont
Teeth of frog------------->acrodont, polyphyodont, homodont
Tusk of elephant is modified upper incisor and tusk of walrus is modified canine.
Enamel is hardest substance in body.
Ectodermal origin and secreted by amyloblast cell.
Dentine is mesodermal in origin and secreted by odontoblast cell.
- Man------------->2 1 2 3/ 2 1 2 3 (adult 20+)
- Man-------------> 2 1 0 2/ 2 1 0 2 (Child)
- Rabbit------------->2 0 3 3 / 1 0 2 3
Tongue
endodermal origin
Divided into oral(2/3) and pharyngeal (1/3) by sulcus terminalis.
Nuhn’s gland/ Ebner’s gland / Weber glans or mucus secreting gland on upper surface of tongue.
- Filliform------------->small and many (No taste buds)
- Fungiform------------->Mushroom shaped, medium, less
- Foliate-------------> in rabbit (man absent)
- Circumvallate------------->largest, least, posterior
Sweet------------->tip
Salt------------->middle
Sour------------->side
Bitter------------->posterior
3 pairs of salivary gland in man, 4 pairs in rabbit.
Parotid------------->stenson’s duct(Largest in size)
Sub-maxillary/sub-mandibular------------->wharton’s duct(maximum secretion)
Sub-lingual------------->duct of ruvinus
Infra orbital salivary gland
Epiglottis absent in frog.
Oesophagus
Peristalsis, only mucous gland, voluntary and involuntary also mixed
Stomach
Peritoneal covering is ometum. Folds are rugae.
Fundus absent in frog.
- Oxyntic/parietal cell------------->HCl
- Zymogen/peptic/chief cell------------->pepsinogen, pro-renin, lipase
- Mucous/goblet cell------------->Mucus
- Argentaffin cell------------->Somatostatin(deactivate gastric gland)
- G-cell------------->Gastrin(activate gastric gland)
Intestine
Duodenum------------->Brunner’s gland(only in duodenum)
Common bile duct open anteriorly and pancreatic duct in distal part.
In human hepato-pancreatic duct open in middle of duodenum.
Peyer’s patches------------->phagocytic cell of intestine
Crypts of Liberkuhn has parieth cell secreting lysozyme which kill germ/bacteria.
Succus entericus------------->Secretion of Crypts of Lieberkuhn
Sacculus rotundus is terminal bulb like part of ileum in rat and rabbit(not in man).
Colon
Pouch haustra
E. coli present I colon (vit B2, B12, K2 synthesis)
Rectum is retroperitoneal (like oesophagus tunica adventia is outermost layer.)
Muscularis layer consists of inner circular and outer longitudinal layer except in stomach.
Liver lobes
- 3 frog @(4 letters -1)
- 4 human @(5 letter -1)
- 5 rabbit @(6 letter -1)
Glisson’s capsule -------------> characteristic feature of mammal
Billirubin------------->yellow
Billiverdin------------->green
Pancreas
Wirssung’s duct is main and sentorni is accessory pancreatic duct.
Hepatopancreatic duct has spincter of oddi and ampulla of vater.
α-cell------------->glucagon (increase sugar level)
β-cell------------->insulin
δ -cell------------->somatostatin(inhibit gastrin and secretin)
pp-cell------------->polypeptide(inhibit pancreatic juice)
CIRCULATORY
Human heart is myogenic, frog’s heat is neurogenic. The wall of heart consist of pericardium, myocardium and endocardium (outside to inside).
Area of chest overlying the heart is called pericardium.
Coronary sulcus divides heart into right auricle larger than left auricle.
In right auricle 2 venecava in man and 3 venecava in rabbit open.
During embroynic stages in place of inter-atrial or inter-auricular septum, septum primum and septum secondum are present having a gap called foramen ovalis.
A flap called Eustachian flap is present from the opening of inferior venecava up to foramen ovalies which prevent the entry of blood in the fetal heart to lungs.
During birth there is closure of foramen ovalis but thre remains depression on both sides, depression on right atrium is fossa ovalis and on left is fossa lunata.
Right auricle-ventricle- tricuspid valve
Left auricle-ventricle- bicuspid valve
Semilunar valve controls backflow of blood from aorta and pulmonary artery
Wall of ventricles have muscular bundles called columnae cornea or papillary muscle. Bicuspid and tricuspid valves are attached to papillary muscle through cordae tendinae.(absent in frog, prevent backflow of blood from valve)
Moderator band present in right ventricle.
Ear like appendages attached to atria is auricle.
At places of crossing the pulmonary aorta and caroticosystemic aorta are connected by muscular band known as ligamentum arterosum which during embryonic stages was represented as ductus arteriosum or duct of botalli.
Sinus venosus (dorsal side of frog) and conus arteriosus (obliquely upon ventral surface of right atrium in frog) are accessory chambers in heart of lower vertebrates (fishes and amphibians)
In rabbit sinus venosus is formed in embryo but later becomes of right atrium.
Cardiac centre is medulla oblongata
Impulse originated in SA node--------------->Wall of auricle-------------------> auricle contracts --------->AV nodes- sends impulses --------->Bundle of his- Right & Left bundle branch --------------->Purkinje fibers --------------->Wall of ventricles-------------> ventricle contracts
Cardiac cycle in human = 0.8 sec
In frog = 0.94 sec
Heart sound: 1st lubb, 2nd dub
Athletes have low heart rate ( Bradycardia)
Pulmonary vein, Inernal jugular vein, Sinuses of brain and Superior venecava are the veins without valve.
Renal portal system present in frog and human hepatic portal system in human
First branch of aorta is coronary artery and first branch of arch of aorta is Brachiocephalic artery.
Umbilical cord has two artery and one vein. Albumin synthesized by liver.
Cistern chili/ receptaculum chili- second heart present below diaphragm and collect lymph from posterior part of body.
Phrenic artery supply blood to diaphgram.
Anterior abdominal vein ( formed by union of right and left pelvic vein) present in frog is absent in rabbit and mammal.
Diaphragm penetration T8 – Venecava
T10- Oesophagus
T12- Thoracic Duct Aorta
Frog heart beat – 64 per minute
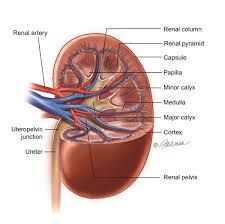
EXCRETORY SYSTEM
Mammalian kidney is metanephric.
Right kidney lower than left because of liver in human. Opposite in case of rabbit
Archeonephric- Schistomata eg. Hag fish
Pronephric- Fish and tadpole stage
Mesonephric- Adult amphibia an lung fish
Metanephric- Reptiles, Aves and Birds
Kidney receive 25% of cardiac output per minute
Glomerulus
Bowman’s capsule formed by simple squamous epithelial cells. Boot-shaped podocyte cells present in visceral layer
PCT- - simple cudoidal epithelium & brush border cells
- Maximum absorption
Loop of Henle
- Decending limb- squamous epithelium
- Water absorption
- Ascending limb- cuboidial epithelium
- Ions absorption no water entry
DCT
- Reabsorption of water under influence of ADH
Deficiency of ADH causes excess urination called dieresis (insipidus diabetes)
All excretory organ originated from mesoderm except urinary bladder originated from endoderm.
Urinary baldder lined with trantitional epithelium.
Aminotelic- Unio, Limax, Star fish
Ammonotelic- Bony Fish, tadpole
Uricotelic- Birds, inscets, reptiles
Ureotelic- Mammals, frog, cartilaginous fish
Due to: Urine yellow(urocrome), faeces brown (stercobilin)
Rabbit coprophagus
Hormones secreted by kidney-
- Renin
- Erythropoietin
- Vit. D
Urethrisis common in female
Net filtration pressure= GHP-BOP-CHP
= 75-20-20
25 mm of hg
Inlammation of urinary bladder- Cystitis
PCT absorb- AG VET (Amino acid, Glucose, Vitamin) Water, Na+, k+, Ca+ absorption
DCT absorb- ADH (water,) Aldesterone(Na+), Active absorption of Na+ & Secretion of K+
PCT secrete- Cretaine, Hydrogen, Hippuric acid, ammonia
DCT secrete- Bicarbonate, Potassium, Hydrogen, Ammonia
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
Male reproductive system
Abdomen, testes connected by inguinal canal
- Human ---------------> Scrotal Testes
- Elephant, Whale ---------------> Abdominal testes
- Rabbit ---------------> Migratory testes
Interstitial cells of leydig secete testosterone under influence of leutenizing hormone (LH)
Condition in which testes do not descend into the scrotum is called crypto orchidism
Spermatogenesis
Germinal epithelial cell
One primary spermatocyte = Four Sperm
One secondary sperm atocyte =Two Sperms
Spermatogonia (2n) ---------------> Primary spermatocytes (2n) ---------------> Secondary spermatocyte (n) ---------------> Spermatids (n) ---------------> Spermatozoa (n)
Spermatids undergo spermeogenesis to form spermatozoa
Sperms remain alive and retain their ability to fertilize ovum from 24 to 48hrs after being released in female tract
Capacitation ---------------> Sperm develop capacity to fertilize ovum that develops in fallopian tube
Acrosome formed from golgicomplex contains digestive enzymes spermlysine (Hyaluronidase)
Middle piece (Mitochondria) contain mitochondria surrounding axonema called nabenkern sheath and cytoplasm around mitochondria is manchette
Scortum is made up of dartos muscle
Seminiferous tubules ---------------> Rete Testes (Straight Tubules) ---------------> Ductus epididymis (Wolffian Duct) --------------->Ductus deferens (Vas deferens) ---------------> Ejaculatory duct
Accessory sex glands
Seminal vesicles (Alkaline including fructose )
Prostrate gland (Acidic )
Cowper’s gland (Bullbourethral gland ) (Alkaline seceration neutralize acid from urine)
Surgical removal of prepuce in muslims and jews is circumcision.
Left testes is lower than right.
Perineal or rectal glands are absent in man.
Female reproductive organ
Ovule
- During birth---------------------> stop at diplotene stage
- Ovulation---------------------> stop at meiosis II (metaphase- II)
Estrogen secreted by granulosa cells of griffin follicle.
Progestrone secreted by corpus luteum.
Ovum dies after 24 hours if not fertilized, resulting menstruation and corpus luteum degenerate into corpus ablicans.
Ovum if fertilized gets implanted at endometrium at the blastocyst stage and placenta secrete Human Chorionic Gonadotropin(HCG) which maintain corpus luteum after pregnancy.
Menstrual phase occur in primates and oestrous cycle occur in non-primates.
- 1 to 4--------------------->Menstrual/bleeding phase
- 5 to 14 --------------------->Follicular , proliferative phase, estrogen
- 15 to 28 ---------------------> Luteal, secretory, progestron, constant(about 14 days)
- Infundibulum
- Ampulla---------------------->site of fertilization
- Isthmus
Isthmus separate body and cervix.
Uterus histology
- Perimatrium
- Myomatrium
- Endomatrium
Endomatrium consists of stratum basilis and stratum functionalis.
Stratum functionalis sloughs off during menstruation.
Upper uterus lined by columnar epithellum and lower part of uterus lined by squamous epithelium.
The common area (transition zone) is common site of cervical cancer.
Uterine prolapse is common among multiple births and aged womwn.
Pap’s smear test is screening test for cervical cancer.
Vagina lined by non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium.
Hymen often torn during first coitus.
Bartholin’s gland secrete alkaline fluid which act as lubricant during sexual intercourse.
Homologous organs
| Male | Female |
| Scrotum | Labia majora |
| Spongy(penile) urethra | Labia minora |
| Penis | Clitoris |
| Cowper’s/ Bulbourethral gland | Bartholin’s/ greater vestibular gland |
| Prostrate gland | Paraurethral (Skene’s gland) |
NERVOUS SYSTEM
Brain
Cranial meninges (Out to in)
- Duramater
- Arachnoid
- Piamater
CSF secreating folding or stretches called choroid plexuses and arachnoid villi helps in CSF absorption.
Communication between ventricles
- Each lateral ventricle------------(Intraventricular foramen/foramen of monro)---------->3rd ventricle
- 3rd ventricle-------------(cerebral aqueduct of sylvinus/aqueduct of sylvinus)------------->4th ventricle
CSF leave ventricle and enter subarachnoid apace through two lateral foramina of Luschka and median foramen of Magendie in fourth ventricle.
Piamater and Arachnoid mater are together called leptomeninges.
- Sub Dural Space-(Arachnoid and Duramater)--------> filled with serous fluid
- Sub Arachnoid Space-(Duramater and Piamater)--------> Filled with CSF
Grey matter- Outer
White matter- Inner
Mid brain--------> 4 lobes----------------> Corpora quadrigemina
Lession in broca’s area results in inability to produce words and speech(in Frontal lobe).
Olfactory lobe distinct in rabbit and attached to anterior end of cerebrum but indistinct in human.
Limbic system- the emotional brain
Amaygdala is considered as “Window of Limbic System”.
Thalamus
Receive and send sensory impulses.
Hypothalamus
Functions @SEAT2
Sex, Sleep
Emotion, Endocrine
Appetite, ANS
Thirst, Temperature
Hypothalamus joins pituitary gland by infundibulum.
Hemiplega--------> Half paralyzed--------->Opposite frontal lobe damaged.
Cerebral hemisphere(cerebral cortex) consistsof gyri(raised), sulsi(depression).
Hemisphere are connected by myelinated nerve called corpus callosum. Presence of corpus callosum is the exclusive character of mammal.
Corpora quadrigemina
-----> 4 swelling mammals
Mid-brain of Frog has two oval optic sacs.
Pons
Apneustic and pneumotaxic center in this area helps to control respiration.
4th ventricle lies between surface of pons and cerebellum.
Medulla Oblongata
Respiratory center, Cardiac center and vasomotor center.
Cerebellum
Maintain body balance, muscle coordination.
Alcohol suppress cerebellum temporarily.
Peripheral nervous system
Cranial nerves
12 pairs of cranial nerves in mammals, 10 pairs of cranial nerves in fishes and amphibians.
Vagus control heartbeat(parasympathetic)
Largest and thickest------------> Trigeminal(Dentist nerve)
Smallest---------------->Abducens
Thinnest---------------->Trochlear
Longest------------------->Vagus
Spinal Cord and nerves
Grey matter---------------> In
White matter--------------> Out
Butterfly or H-shaped(Spinal Cord).
Posterior horn or dorsal horn consists of sensory neurons whereas anterior horn or ventral horn consists of motor neurons.
Spinal nerves--------------------> 31 pairs(All mixed nerves)
Cervical--------------> 8 pair
Thorax--------------->12 pair
Lumbar---------------> 5 pair
Saccral---------------->5 pair
Coccygeal-------------> 1 pair
Frog has 10 pairs of spinal nerves and in Rana tigrina it is 9 pairs.(37 pairs in rabbit).
Accessory and Hypoglossal(Cranial nerves). Absent in frog.
Spinal cord of frog tapers posteriorly in Urostyle as Filum terminale or cauda equina.
Spinal nerve passes through gland of Swammerdam(Ca+ rich) after emersing from spinal cord.
Autonomic nervous system
| Parasympathetic | Sympathetic |
| (cranio-saccral) | (thoraco-lumbar) |
| Acetocholine | Noradrenaline |
| Penis erection | Semen ejaculation |
Nerve impulse
Resting potential (Polarized)----------------> -70mV
Active potential (Depolarized)---------------> 45mV
Repolarization----------------------------------> -70mV
Alzheimer’s disease(Dementia)------------->hyposecreation of acetycholine (old age disease)
SKELETAL SYSTEM
Axial
- Skull-22
- Ribs-12 pairs
- Sternum-1
- Vertebrae- 26
- Hyoid bone-6
Skull
- Cranial-8
- Facial-14
Cranial bone
Virus Can Not Make My Pet Zebra Laugh.
V and M------------>Vomer and Mandibular are only unpaired bones in face.
Vertebrae
- C7H12L5S5Co4 (Baby)
- C7H12L5S1Co1 (Adult)
Rabbit skull
- Cranial-------->Frontal, Parietal, Occipital segment
- Facial----------> Eye, nose, ear, capsule + Jaw
Foramen magnum surrounded by supraoccipital(1), baso-occipital(1) and exoccipital(2) of occipital segment.
Sella turcica is present in basisphenoid as small depression to lodge pituitary gland.
Ethmoid bone(Cribiform plate) from where olfactory and optic nerve pass is a part of frontal segment.
Optic capsule----------->Separated by interorbital septum so called triploblastic condition.
Auditory capsule--------> Tympanic bulla is flask shaped bone present between basisphenoid and squamosal .
Periotic bone is compound bone.
Olfactory capsule
- Separated by mesethmoid into cavities
- Turbinal also called scroll bone or air conditional. (Conchae in human).
Squamosal and maxilla connected by jugal called zygomatic arch. Zygomatic process is of squamosal bone.
Dentary------------>Lower jaw (Half of lower jaw – Ramous)
Diastema-------------> Gap between incisor and premolar
Rodenia(Rat order) and Lagomorpha(Rabbit order)---------------> Have diastema
Suspensorium (Lower jaw join to upper jaw)
- Craniostyllic-Rabbit
- Autostylic-Frog
Rabbit vertebrae-------------> C7H12-13L6-7S4Co16
Dental formula-------------> 2033/1023 (Rabbit), 2123/2123(Man)
Acoelous---> Bone, Flat posterior and anterior
Procoelous----> Bone, front concave, rear convex
Amphicoelous----> Both surface concave
Vertebrae-----------> Man(26), Rabbit(45 to 47) , Frog(10)
Atlas--------> No prezygapophysis
Typical vertebrae of frog (2-7)---------> Acoelous + 9th vertebrae
8th vertebrae of frog is Amphicoelous.
Cervical vertebrae-------------> 7 in all mammals except Sea cow (6), Sloth(8)
Atlas--------------->Neural spine reduced, No centrum, both zygapophysis
Axis------------------> Odontoid process(Dens), Post zygapophysis only present
Typical cervical-----------------> Transverse process + Short pointed neural spine, both zygapophysis
Thoracic vertebrae----------------> 1st has long backwardly directed neural spine
Lumbar vertebrae-------------------> Anterior lumbar has hypapophysis
Sternum--------------> Breast bone
Xiphoid cartilage
- Manubrium(1)
- Gladiolus(2-6)
- Xiphisternum (7) bear xiphoid cartilage
Ribs and thoracic vertebrae
- C to C Centrum to Capitulum)
- T to t (tuberculum to transverse process)
Pectorial girdle
- Coracoid process
- Acromian process
- Metacromian process
Pelvic girdle ---------------> Ilium + Ischium = Acetabulum
Only pubis doesnot form acetabularia.
Largest foramen of body(between pubis and ischium)---------------------> Obturator foramen
Cotyloid between ilium and ischium.
Digital formula
| Rabbit | Frog | Human | |
| Fore limb | 2,3,3,3,3 | 0,2,2,3,3 | 2,3,3,3,3 |
| Hind limb | 0,3,3,3,3 | 2,2,3,4,3 | 2,3,3,3,3 |
Humerus
Olecranon fossa, Coronoid fossa, Deltoid ridge
Radio-ulna-------> Epiphysis (Tibia-fibula)
Tibia------------> Cnemial crest
Deltoid ligament------------> Ankle joint
Stiffness of joint in old age is due to decrease in synovial fluid
Sprain-------------> Excessive stretching causing twis of pull of ligament.
Bone to bone joining is done by ligament.
Ball and socket joint---------------->Shoulder and hip
Hinge joint---------------->Elbow and phalangeal joint
Pivot joint---------------->Atlas and skull
Saddle joint---------------->Thumb joint
Gliding joint---------------->Radius and ulna
Angular joint---------------->Wrist joint
Knee joint is largest in body
Floating ribs, 2 in human, 3 in rabbit.
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
Nasal cavity lined by pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
Paranasal sinuses are- Frontal sinus, Ethmoid sinus, maxillary sinus, sephenoid sinus
Common site of epistaxis is little’s/ Kiesselbach’s area.
Pharynx is common organ for respiration and digestion.
Eustachian tube connects middle ear and nasopharynx.
Laryx has 9 cartilage (6 types, 3 paired, and 3 umpaired)
- Unpaired cartilage (@ETC) Epiglottis, Thyroid, Cricoid
- Paired cartilage Arytenoid, Cuneiform, Corniculate
- Elastic cartilage Epiglottis, Corniculate, Cuneiform
- Hyanline cartilage (@CAT) Cricoid, Arytenoid, Thyroid
Trachea has C shaped hyaline carilages. Trachea bifurcated at T4 and right bronchi wider, vertical and shorter (@ Right wives)
Alveoli lined by simple squamous epithelium
Type-I alveolar cell à Secrete ACE
Type-II alveolar cell à secrete surfactant
Space between two lungs is media stinum
Lungs
- Human (5) ---------------> Right 3, Left 2
- Rabbit (6) ---------------> Right 4, Left 2
- Frog (1)
Diaphragm supplied by phrenic artery, characteristic feature of mammal and
Flattens during inspiration
Dome shape during expiration
One molecule of Hb can carry four molecules of oxygen
One gram of Hb can bind 1.34 ml of oxygen
- Anoxia ---------------> Absense of o2
- Hypoxia ---------------> Decreased o2 level in blood
- Asphyxia ---------------> Suffocatio as a result of airway obstruction
Oxygen Hb dissociation curve
- Show relationship between percentage saturation of Hb with oxygen and partial pressure of oxygen
- It is sigmoid shaped curve
Right shift
- Decreased affinity of Hb for o2, more release of o2 to tissue
- Increase H+ ion
- Decrease pH
- Increase pCO2 of blood
- Increase temperature
- Increase 2,3 DPG (Secerated by RBC in high altitude)
Bohr’s effect
---------------> High o2 concentration causes decreased affinity of Hb for o2
Haldane effect
---------------> High oxygen concentration enhances the unloading of co2
Chloride shift (Hamburger shift)
---------------> Exchange of HCO3- and Cl- across the membrane of RBC
- Tidal Volume ---------------> 500ml
- Inspiratory reserve volume ---------------> 3100 ml
- Expiratory reserved volume ---------------> 1200ml
- Residual volume ---------------> 1200 ml
- Vital capacity ---------------> IRB+ ERV+ TV = 4800ml
- Dead space ---------------> 150 ml
- Total lung capacity ---------------> VC+RV = 6000ml
Tachypnoea ---------------> Increase in respiratory rate
Dyspnoea ---------------> Difficulty in breathing
Orthopnoea ---------------> Difficulty in breathing while laying down
Haemoptysis ---------------> Coughing out of blood
Haemotemasis ---------------> Vomiting out of blood
Hematochaezia ---------------> Passage of fresh blood in stool
Malena ---------------> Passage of (Not fresh) altered blood in stool
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
Hormone
- Coined by Starling
- Huxley called them chemical messengers
- First hormone discovered was secretin by Bayliss and Starling.
- First protein to be synthesized in laboratory was insulin by Banting and Best.
Father of endocrinology------------>Addition
1st endocrine disease------------>Adrenal cortes destruction called Addition’s disease.
Hormones are not stored (except thyroxine).
Released by ductless glands and poured directly into the blood.
Pituitary gland (Hypophyseal gland)
Anterior
- FSH
- LH
- ACTH
- TSH
- Prolactic------------>only +ve feedback mechanism
- Growth hormone
Intermediate
- MSH
Posterior
- ADH
- Oxytocin
Anterior (adenohypophysis) connected to hypothalamus by blood vessel and posterior (neurohypophysis) by nerves.
Pars intermedia or intermediate lobe is rudimentary(vestigial) in human.
If Pituitary gland is surgically removed, blood level of sodium falls and potassium rises.
Neurohypophysis is not true endocrine gland as it stores and release hormone of hypothalamus and doesn’t secrete it’s own hormone.
ADH related to concentration of urine. It’s hyposecretion results in diabetic insipidus.
Oxytocin(milk ejection hormone). Induce contraction of mammary gland and muscle of uterus inducing labour pain for child birth.
Thyroid gland
Largest endocrine gland homologous to endostyle of lower chordates.
Butterfly shaped and bi-lobed. Two lobes connected by ‘isthmus’.
Thyroid gland develops from foramen caecum situated at the floor of tongue. Thyroid composed of spherical sacs called thyroid follicles lined by simple cuboidal epithelium.
Hashimotos diease--------------------> Production of antibody against thyroid antigen causes destruction of thyroid thyroid called suicide of thyroid.
Parafollicular cells secrete Calcitonin which lowers the amount of calcium and phosphate in blood.
Parathyroid gland
Present in all vertebrates except fishes.
a.Oxyphil cells
b.Chief cells
Parathormone/ collip’s hormone-------------------->Regulate Ca and PO4 metabolism-------------------->Hypersecretion {Osteomalacia/osteoporosis(adult)} and {Ricket(children)}
Hyposecretion-------------------->Tetany
Adrenal gland
a.Cortex(80%)-------------------->3S{Sugar metabolism, Salt retention, Sexual activity}
b.Medulla(20%)-------------------->3F{Fright, Flight, Fight}
Medulla--------------------->Catecholamines(Epinephrine, Norepinephrine, Dopamine)
Mineralocorticoid (conserve Na and eliminate K)
Glucocorticoid ( increase blood glucose level)
Gynecomastia ( Female character in male) and virility (male character in female).
Pineal gland
Located at the posterior portion of roof of third ventricle.
Also called Brain sand (Ca and Mg salt deposited).
Also called epiphysis cerebri/seat of soul/ reminant of third eye).
3 hormones (Melatonin, serotonin and adrenoglomerulotropin)
Melatonin antagonistic to MSH of pituitary.
Serotonin increases blood pressure and adrenoglomerulotropin stimulate adrenal cortex to secrete aldosterone.
Thymus Gland
Bilobed lymphoid organ situated in front of heart in upper part of sternum.
Throne of immunity or training school of T-lymphocyte or master gland of immunity.
Hormones-------------------> thymosin and thymopoietin.
Pancreas
2nd largest Gland, leaf like structure
Endocrine part
Islets of Langerhans
α-cell----------------->Glucagon
Increase blood sugar level
β-cell-----------------> Insulin
Insulin contain 51 amino acid.
Hyposecretio of insulin results in diabetis mellitus.
δ-cell-----------------> Somatostatin
Inhibit secretion of glucagon and insulin.
F-cell------------------> Pancreatic polypeptide
Inhibit gall-bladder contractions.
Exocrine gland
- Pancreatic acini
- Secrete pancreatic juice
Stomach
Gastrin----------------->Secreted by G-cells of pyloric gland.
Duodenum
Secretin--------------> Stimulate pancreas to secrete fluid
Pancreo-zymin-------------->Stimulate pancreas to secrete enzyme
Chole-cysto-kinin-------------->Simulate gallbladder to rhythemic contraction and these result in rate of bile in duodenum.
Duocrinin-------------->Stimulate secretion of mucus from Brunner’s gland
Small intestine
Enterocrinin-------------->Stimulate intestinal mucosa to secrete the intestinal juice
Enterogastrone-------------->Retards secretion of gastric juice
Villikinin--------------> Stimulate movement of villi for increased absorption.
Kidney
Secrete rennin, erythropoietin and calcitriol.