THERMOMETRY
Mercury is used as thermometric substance in liquid because it has low specific heat and high conductivity.
Absolute zero is 0K and -273.150C.
Magnetic thermometer is used to measure very low temperature near absolute zero.
Thermocouple is used to measure rapidly changing temperature.
Pyrometer is used to measure temperature of Sun.
Gas thermometer are more sensitive than liquid thermometers as gas expands more than liquid.
To measure temperature most accurately we use constant volume gas thermometer.
Helium gas is used to measure very low temperature.
| Scale | LFP | UFP | FI |
| Centigrade | 00C | 1000C | 1000C |
| Fahreinheit | 320F | 2120F | 1800F |
| Kelvin | 273K | 373K | 100K |
| Reumer | 00R | 800R | 800R |
| Rankine | 4920Ra | 6720Ra | 1800Ra |
C-0/100 = F-32/180 = K-273/100 = R-0/80 = Ra-492/180
Relation between centigrade and Fahrenheit
C=5(F-32)/9
Faulty thermometer
Correct scale = Faulty scale
Or, X-LFP/UFP-LFP = Y-LFP/UFP-LFP
THERMAL EXPANSION
α: β: γ=1:2:3
L =L0 (1 + α∆θ )
A = A0 (1 + β∆θ)
V = V0 (1 + γ∆θ )
ρ= ρ0 / (1 + γ∆θ)
F=γ Aα∆θ
Expansion of liquid
γr=γa + γg
fractional change in time period , ∆T/T = ½ α∆θ
temperature increases, length of pendulum increases, time period increases, clock lose time.
If two rods are hollow and another solid heated
---->Through same temperature , equal expansion
----> same heat given , hollow rod expands more.
CALORIEMETRY
Specific heat capacity (S)= H/m∆θ S for water = 4200 J/kg0 C
S=0 for audible change
S = infinity for isothermal change
Specific heat of hydrogen is largest among liquids and gases and water has largest among liquids.
When pressure increases, boiling point increases ( for all liquid)
Melting point decreases ( for ice and rubber)
Melting point increases ( for other solids)
Adding soluble impurities , boiling point increases
Melting point decreases
Latent heat of fusion ----> ice = 80 cal / g
Latent heat of vapourization ---> water = 540 cal/g
Unit of water equivalent is kg/g.
KINETIC THEORY OF GAS
PV = nRT n= m(mass)/M (molecular mass)
R =8.31 J/mol k or , 2 cal/mol k
Boltzman constant (k) = R/NA = 1.38 * 10-23 J/k
pV = nkNAT
pV = NkT (N=nNA =Total number of molecules)
Vrms=√(3RT/M)
Vaverage = 0.921 x Rms velocity =√(8/π x RT/M )
V most probable speed = 0.816 x Rms velocity = √(2 x RT/M)
Translational kinetic energy ,
TK.E = ½ x mV2 rms = 3/2 kTN
HEAT TRANSFER
Q= (kAt(T1-T2 ))/L
where A= area of cross- sectional area, L = length of tube , T1 and T2 is temperature of two different point,
1 calorie = 4.2 joule
Conductor placement ,
In series,
- Heq = H1=H2
- Leq = L1 +L2
- Aeq = A1 = A2
- Req = R1 + R2
In series parallel,
- Heq=H1 + H2
- Leq =L1=L2
- Aeq = A1 + A2
- Req = R1R2/R1+R2
Convection is faster than conduction .
Radiation is fastest mode of heat transfer.
Q =R +A+T
a+r+t = O
when, t=0 , [a=1-r] or [r=1-a]
wien’s displacement law,
λT = 0.289 cm/s
βθϒϒE = sigma * temperature power 4
stefans law = 5.6 * 10 -8 W/m2K4
Newton’s law of cooling ,
(T1-T2) / t = k * ((T1 + T2 )/2 – T0)
[ T1 = initial temperature , T2 = final temperature , t = time taken ,T0 = surrounding temperature]
THERMODYNAMICS
Degree of freedom ,
- Monoatomic gas, f=3
- Diatomic gas , f=5
- Triatomic gas , f= 6
Internal energy (U)=f/2 nRT
Mayor’s formula , Cp – Cv = R
Cp = (1+ f/2 ) *R
Cv = f/2 R
Cp / CV = γ
γ = (1+ 2/f)
isochoric process , V= constant , ∆Q =∆U = f/2 x nRT = n CV ∆T
isobaric process, p= constant , ∆ Q =∆U +∆W = f/2 nR∆T + r∆T
= nR∆T(f/2 +1)
= nCv∆T
Isothermal process, T= constant , ∆Q =∆W = nRT loge(P1/p2)
U = constant
Adiabatic process , Q = constant , ∆U =-∆W
Work done by the system or expansion is taken positive and work done on the system or compression is taken negative.
Adiabatic slope is steeper than isothermal slope.
- Isothermal process , PV= constant
- Adiabatic process , PVγ = constant
First law of thermodynamics ,
∆Q = ∆ U + ∆ W
Second law of thermodynamics
,”heat can never flow from low temperature to high temperature without doing external work.” Clausius statement.
Q1 = Q2 + W
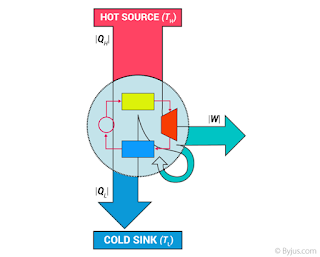
Efficiency of heat engine,
F η = W/Q1 x 100% = (Q1-Q2)/Q1 x 100%
Q1 =Q2 +W
For refrigerator,
Coefficient of performance = Q2/W = Q2/(Q1-Q2)
[Q1/Q2 = T1/T2 ]
Boltzmann constant =R/NA = 1.38 x 10-23 Jk-1
Average K.E. per molecule α Absolute temperature
Critical temperature is that temperature above which a gas can’t be liquefied by pressure only.
Gas possess greatest potential energy.
At boyle’s temperature real gas behaves as ideal gas.
Real gas show ideal behavior at low pressure and high temperature.
Volume of water is maximum at 40 C.
(n1 + n2 )/γmean = n1 /(γ1-1 )+ n2/(γ2 -1 )
Relative humidity increases increases = temperature decreases
Hygrometer measure R.H of air .
Triple point is point at which solid, liquid and gas of matter exist in equilibrium .
For water triple point is( 273.16K , 4.58 mm of Hg.